Felix Immanuel

An Engineer with 6+ years of experience as a Business Analyst. Adept in EDA and Machine Learning. Has a sound knowledge of Agile and Scrum.
View My LinkedIn Profile
Adult Dataset & their Income Analysis
Project description:
The “Adult Dataset has around 32,000 records with various information like age, education, marital-status, occupation, gender, hours per week, country and income information”. From this dataset I have derived various insights and explained them below.
1. Dataset Overview
adt=pd.read_csv('adult.csv')
adt.head()
age workclass fnlwgt ... hours-per-week native-country income
0 39 State-gov 77516 ... 40 United-States <=50K
1 50 Self-emp-not-inc 83311 ... 13 United-States <=50K
2 38 Private 215646 ... 40 United-States <=50K
3 53 Private 234721 ... 40 United-States <=50K
4 28 Private 338409 ... 40 Cuba <=50K
2. Checking for NULL values in the data
adt.isnull().sum()
age 0
workclass 0
fnlwgt 0
education 0
education-num 0
marital-status 0
occupation 0
relationship 0
race 0
sex 0
capital-gain 0
capital-loss 0
hours-per-week 0
native-country 0
income 0
No Null values in this dataset.
3. Changing the column Names
Existing Column Values: Index([‘age’, ‘workclass’, ‘fnlwgt’, ‘education’, ‘education-num’, ‘marital-status’, ‘occupation’, ‘relationship’, ‘race’, ‘sex’, capital-gain’, ‘capital-loss’, ‘hours-per-week’, ‘native-country’, ‘income’],dtype=’object’)
adt.rename(columns={'marital-status' : 'marital'}, inplace = True)
adt.rename(columns={'capital-gain' : 'capgain'}, inplace = True)
adt.rename(columns={'capital-loss' : 'caploss'}, inplace = True)
adt.rename(columns={'hours-per-week' : 'hrsprwk'}, inplace = True)
adt.rename(columns={'native-country' : 'country'}, inplace = True)
Corrected Column Values: Index([‘age’, ‘workclass’, ‘fnlwgt’, ‘education’, ‘education-num’, ‘marital’, ‘occupation’, ‘relationship’, ‘race’, ‘sex’, ‘capgain’, ‘caploss’, ‘hrsprwk’, ‘country’, ‘income’], dtype=’object’)
4. Grouping the “Countries” into Region
There were 42 unique entries in the country column and around 583 entries where unknow.
adt['country'].value_counts()
United-States 29170
Mexico 643
? 583
Philippines 198
Germany 137
Canada 121
Puerto-Rico 114
El-Salvador 106
India 100
Cuba 95
England 90
Jamaica 81
South 80
China 75
Italy 73
Dominican-Republic 70
Vietnam 67
Guatemala 64
Japan 62
Poland 60
Columbia 59
Taiwan 51
Haiti 44
Iran 43
Portugal 37
Nicaragua 34
Peru 31
Greece 29
France 29
Ecuador 28
Ireland 24
Hong 20
Trinadad&Tobago 19
Cambodia 19
Thailand 18
Laos 18
Yugoslavia 16
Outlying-US(Guam-USVI-etc) 14
Hungary 13
Honduras 13
Scotland 12
Holand-Netherlands 1
Name: country, dtype: int64
Grouping all the countries into 4 regions (America, Asia, Europe, Others).
Creating a new column
adt['region']='Asia'
Grouping the countries
adt['region'][adt['country'].isin(['United-States','Canada','Mexico','Puerto-Rico','El-Salvador','Jamaica','Guatemala','Columbia',
'Nicaragua','Trinadad&Tobago','Cambodia','Laos','Outlying-US(Guam-USVI-etc)','Honduras'])]='America'
adt['region'][adt['country'].isin(['Germany','England','Italy','Dominican-Republic','Poland','Iran','Portugal','France','Greece',
'Ecuador','Ireland','Scotland','Holand-Netherlands'])]='Europe'
adt['region'][adt['country'].isin(['?',])]='Others'
Region Overview
adt['region'].value_counts()
America 30475
Asia 870
Europe 633
Others 583
Name: region, dtype: int64
5. Grouping the “Education Entries” into Categories
There were 16 unique entries in the education column.
adt['education'].value_counts()
HS-grad 10501
Some-college 7291
Bachelors 5355
Masters 1723
Assoc-voc 1382
11th 1175
Assoc-acdm 1067
10th 933
7th-8th 646
Prof-school 576
9th 514
12th 433
Doctorate 413
5th-6th 333
1st-4th 168
Preschool 51
Name: education, dtype: int64
Grouping all the education into 3 categories (School, Graduate, Other Education)
adt['edu_category']='School'
adt['edu_category'][adt['education'].isin(['HS-grad','Some-college','Bachelors','Masters','Doctorate'])]='Graduate'
adt['edu_category'][adt['education'].isin(['Assoc-voc','Assoc-acdm'])]='OthrEDU'
Education Category Overview
adt['edu_category'].value_counts()
Graduate 25283
School 4829
OthrEDU 2449
Name: edu, dtype: int64
6. Grouping the “Occupation” into Job Categories
There were 15 unique entries in the occupation column.
adt['occupation'].value_counts()
Prof-specialty 4140
Craft-repair 4099
Exec-managerial 4066
Adm-clerical 3770
Sales 3650
Other-service 3295
Machine-op-inspct 2002
? 1843
Transport-moving 1597
Handlers-cleaners 1370
Farming-fishing 994
Tech-support 928
Protective-serv 649
Priv-house-serv 149
Armed-Forces 9
Name: occupation, dtype: int64
Grouping all the occupation into 2 categories (officeJobs, fieldJobs)
adt['jobCategory']='officeJobs'
adt['jobCategory'][adt['occupation'].isin(['Craft-repair','Sales','Transport-moving','Handlers-cleaners','Farming-fishing'])]='fieldJobs'
Job Category Overview
adt['jobCategory'].value_counts()
officeJobs 20851
fieldJobs 11710
Name: occu, dtype: int64
7. Processing “Hours-per-week” Column
Checking for Outliers in the “Hours-per-week” Column.
plt.boxplot(adt['hrsprwk'])
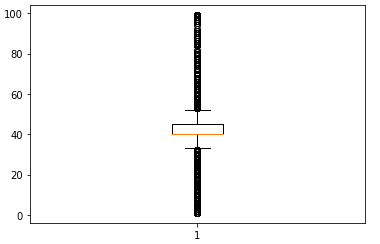
Treating the Outliers
p25=adt['hrsprwk'].quantile(.25)
p75=adt['hrsprwk'].quantile(.75)
iqr=p75-p25
lowerrange=p25-(1.5*iqr)
upperrange=p75+(1.5*iqr)
adt['hrsprwk'][adt['hrsprwk']<lowerrange]=np.nan
adt['hrsprwk'][adt['hrsprwk']>upperrange]=np.nan
adt['hrsprwk'].isnull().sum()
adt['hrsprwk'].fillna(0,inplace=True)
After treating the Outliers.
plt.boxplot(adt['hrsprwk'])
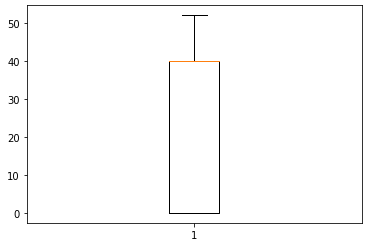
8. Getting Dummies from the newly created column for “Random Forest ML Algorithm”
Getting dummies for “Region”.
r=pd.get_dummies(adt['region'])
adt=pd.concat([adt,r], axis=1)
Getting dummies for “Gender”.
s=pd.get_dummies(adt['sex'])
adt=pd.concat([adt,s], axis=1)
Getting dummies for “Education Category”.
e=pd.get_dummies(adt['edu_category'])
adt=pd.concat([adt,e],axis=1)
Getting dummies for “Gender Category”.
o=pd.get_dummies(adt['jobCategory'])
adt=pd.concat([adt,o],axis=1)
Getting dummies for “Workclass”.
wk=pd.get_dummies(adt['workclass'])
adt=pd.concat([adt,wk],axis=1)
Getting dummies for “Marital Status”.
ma=pd.get_dummies(adt['marital'])
adt=pd.concat([adt,ma],axis=1)
Getting dummies for “Family Relationship Status”.
re=pd.get_dummies(adt['relationship'])
adt=pd.concat([adt,re],axis=1)
Columns list before getting dummies
adt.columns
Index(['age', 'workclass', 'fnlwgt', 'education', 'education-num', 'marital', 'occupation', 'relationship', 'race', 'sex', 'capgain', 'caploss', 'hrsprwk', 'country', 'income'], dtype='object')
Columns list after getting dummies
adt.columns
Index(['age', 'workclass', 'fnlwgt', 'education', 'education-num', 'marital', 'occupation', 'relationship', 'race', 'sex', 'capgain', 'caploss', 'hrsprwk', 'country', 'income', 'region', 'Female', 'Male', 'edu', 'occu', 'Graduate', 'OthrEDU', 'school', 'fieldJobs', 'officeJobs', 'America', 'Europe', 'Others', 'asia', 'Federal-gov', 'Local-gov', 'Never-worked', 'Private', 'Self-emp-inc', 'Self-emp-not-inc', 'State-gov', 'Without-pay', 'Divorced', 'Married-AF-spouse', 'Married-civ-spouse', 'Married-spouse-absent', 'Never-married',
'Separated', 'Widowed', 'Husband', 'Not-in-family', 'Other-relative', 'Own-child', 'Unmarried', 'Wife'], dtype='object')
9. Dataset Insights
The below insights are about the people who earn more according to each category.
1. Income comparison according to a “Region”
People who lives in the American region earns more than any other people in the world.
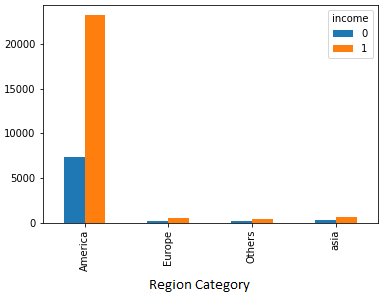
2. Income comparison of an individual according to his “Family Status”
The Person who is not in a family earns more money than any other category and in a family Husbands earn more than all.
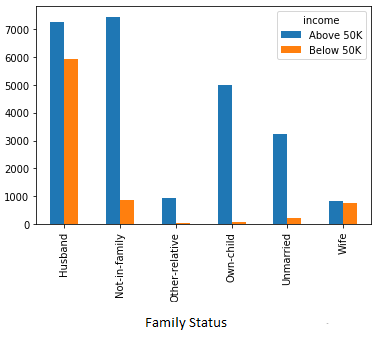
3. Income comparison according to an individuals “Marital Status”
People who is not married earns more than any other marital status.
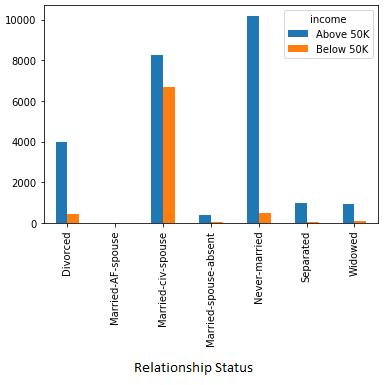
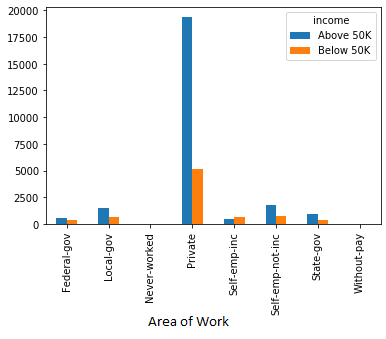
4. Income comparison according to the “Job Sector”
People who work in the private sector earns more than the people who works in the government & other areas.
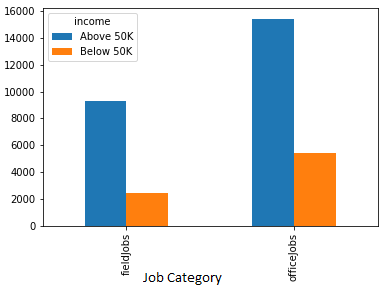
5. Income comparison as per “Job”
People who are working in professional office jobs earn more than the people who work in field jobs.
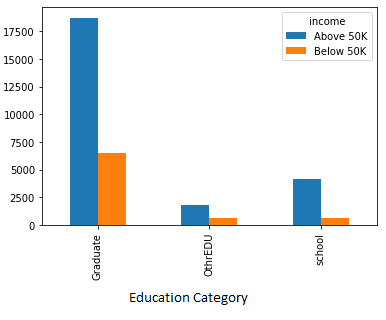
6. Income comparison as per the “Education”
Graduates earn more than the people who didn’t complete graduation.
10. Building Model (Random Forest ML Algorithm)
1. Importing the dataset
X = adt[['Female','America','Europe','asia','Federal-gov', 'Local-gov', 'Never-worked', 'Private', 'Self-emp-inc', 'Self-emp-not-inc', 'State-gov', 'Divorced', 'Married-AF-spouse', 'Married-civ-spouse', 'Married-spouse-absent', 'Never-married', 'Separated','Husband', 'Not-in-family', 'Other-relative', 'Own-child', 'Unmarried']]
y = adt[['income']]
2. Splitting the dataset into the Training set and Test set
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size = 0.25, random_state = 0)
3. Fitting Random Forest to the Training set
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
classifier=RandomForestClassifier()
classifier.fit(X_train,y_train)
4. Predicting the Test set results
y_pred = classifier.predict(X_test)
5. Prediction Accuracy
print("The train accuracy " , classifier.score(X_train,y_train)*100)
print("The test accuracy " , classifier.score(X_test,y_test)*100)
The train accuracy 98.29
The test accuracy 81.88